Cross Currency Pairs A Guide for Investors Introduction The foreign...
Read MoreUnderstanding the Risk and Return Profile
A Guide for Strategic Investing
Table of Contents
- What Exactly Is a Risk and Return Profile?
- How Do Different Asset Classes Compare in Terms of Risk?
- Why Is Standard Deviation Critical for Measuring Volatility?
- How Does Diversification Alter an Investor’s Risk Profile?
- What Role Do Risk-Adjusted Ratios Play in Portfolio Selection?
- How Can Structured Products Engineer a Custom Risk-Return Outcome?
- Conclusion: Building a Resilient Portfolio
Investing is rarely a linear path to profit; it is a calculated negotiation between the desire for growth and the tolerance for uncertainty. For investors in the Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) and the broader UAE, distinguishing between “risk” and “return” is not enough. One must understand the Risk and Return Profile—the unique behavioral signature of an investment that dictates how it is likely to perform under various market conditions.
Whether you are an institutional client managing family office funds or an individual exploring global equities, defining this profile is the first step toward aligning your capital with your financial goals.

What Exactly Is a Risk and Return Profile?
A Risk and Return Profile is a comprehensive evaluation of an investment’s potential for financial loss against its potential for gain. It is not merely a label of “high” or “low” risk; it is a spectrum that considers the probability of negative outcomes, the magnitude of potential volatility, and the time horizon required to achieve expected returns.
In professional wealth management, this profile serves as a blueprint. It helps investors determine if the “price” of an investment—in terms of sleepless nights or potential capital erosion—is worth the expected reward. For instance, a government bond typically has a conservative profile: low volatility and modest returns. In contrast, emerging market derivatives may offer a high-octane profile with significant upside but equally substantial downside exposure.
How Do Different Asset Classes Compare in Terms of Risk?
Every asset class carries a distinct DNA regarding how it reacts to economic shifts. Understanding this hierarchy is essential for constructing a balanced portfolio.
- Fixed Income (Bonds): generally sits at the lower end of the risk spectrum. Sovereign debt from stable economies is often used for capital preservation, though corporate bonds can introduce credit risk in exchange for higher yields.
- Equities (Stocks): occupy the middle-to-high ground. Owning shares in blue-chip US companies or growth-focused sectors involves accepting market fluctuations. The return potential is theoretically unlimited, but the investor absorbs the full volatility of the market.
- Derivatives (Futures & Options): are often at the higher end due to leverage. Instruments like Global Futures & Options allow traders to hedge or speculate, but the use of margin can amplify both gains and losses, significantly altering the risk profile.
- Forex (FX): The currency market is highly liquid but volatile. Trading Spot FX & CFDs involves navigating geopolitical events and central bank policies, creating a profile suited for active traders rather than passive “buy-and-hold” investors.
Ready to Diversify Your Portfolio?
Explore our range of global asset classes
Why Is Standard Deviation Critical for Measuring Volatility?
When analysts discuss “risk,” they are often referring to volatility—the degree to which an asset’s price swings around its average. Standard deviation is the statistical tool used to quantify this swing.
If an investment has a high standard deviation, its price moves erratically. This erratic behavior defines a “high-risk” profile because the probability of needing to exit the investment during a downturn is higher. For investors managing Institutional Services or family offices, keeping standard deviation within acceptable limits is often more important than chasing the highest possible raw return. It ensures that the portfolio’s value remains relatively stable, facilitating liquidity needs and long-term planning.
How Does Diversification Alter an Investor's Risk Profile?
Diversification is the only “free lunch” in finance because it can lower a portfolio’s overall risk profile without necessarily sacrificing expected returns. This works through correlation—or rather, the lack of it.
By combining assets that do not move in perfect lockstep, such as US Stocks, ETFs & ADRs with commodities like Gold or Silver, investors can smooth out the ride. When equities dip due to economic cooling, commodities might rise as a hedge against inflation. This interplay reduces the aggregate standard deviation of the portfolio, creating a more efficient risk and return profile than holding any single asset in isolation.
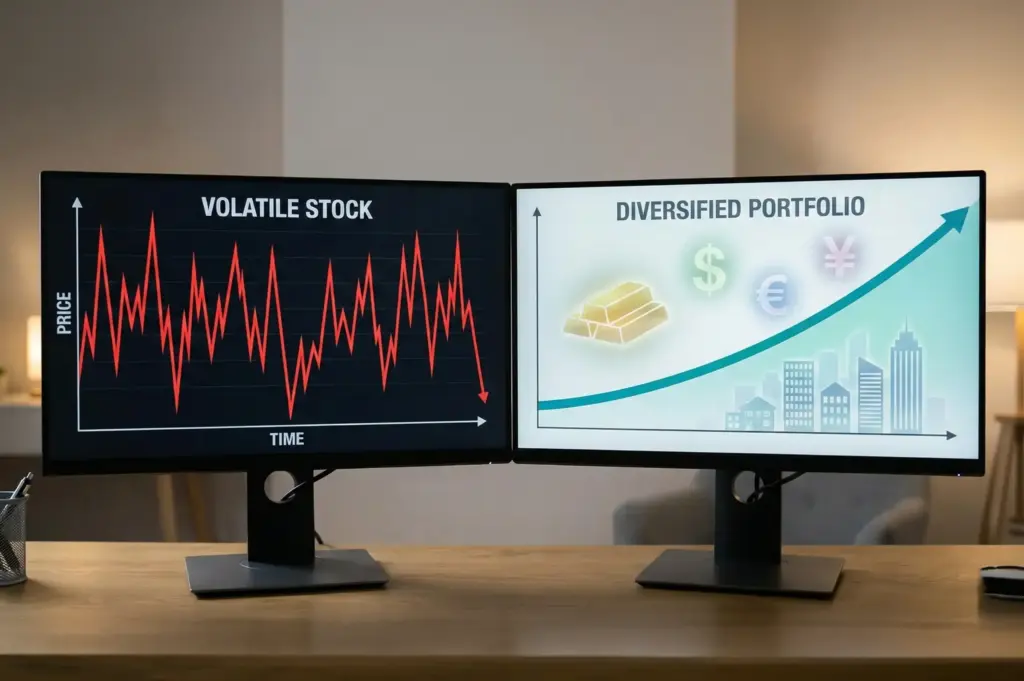
What Role Do Risk-Adjusted Ratios Play in Portfolio Selection?
Raw returns can be deceptive. A 20% return sounds excellent, but if it required risking a 50% drawdown, the trade-off may not be favorable. This is where risk-adjusted metrics like the Sharpe Ratio come into play.
The Sharpe Ratio measures the excess return generated for every unit of risk taken. A higher ratio indicates a more efficient investment. For sophisticated investors, calculating these ratios is vital when comparing Wealth Management strategies. It answers the critical question: “Am I being adequately compensated for the anxiety and uncertainty I am enduring?” If two funds offer the same return, but one has half the volatility, the latter has a superior risk and return profile.
How Can Structured Products Engineer a Custom Risk-Return Outcome?
One of the most powerful ways to modify a risk profile is through financial engineering. Structured Notes allow investors to reshape the standard payoff of an asset to fit specific views.
For example, an investor might desire exposure to the S&P 500 but fears a market correction. A standard equity investment offers no safety net. However, a Capital Protected Note can change this profile entirely, offering participation in the upside while guaranteeing the principal amount at maturity (subject to issuer credit risk). Alternatively, Yield Enhancement notes can generate income in flat markets where traditional equities might stagnate. These tools essentially “bend” the risk-return line to suit the investor’s unique tolerance
Customize Your Market Exposure
Discover how Structured Notes can protect your capital.
Conclusion: Building a Resilient Portfolio
The search for the perfect investment is a myth; the search for the optimal Risk and Return Profile is the reality of successful wealth management. By identifying your tolerance for volatility and understanding the statistical characteristics of different asset classes—from the leverage of derivatives to the engineered safety of structured products—you can construct a portfolio that is robust enough to weather market storms.
At PhillipCapital DIFC, we provide the global access and institutional-grade tools necessary to execute these sophisticated strategies. Whether your goal is aggressive growth or capital preservation, clarity on your risk profile is your most valuable asset.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
No. In finance, “risk” refers to uncertainty, not a guaranteed payout. Taking on higher risk only increases the potential for higher returns; it simultaneously increases the probability of significant losses. If a high return were guaranteed, it would not be considered risky.
A widely accepted benchmark for active traders is 1:2 or 1:3. This means for every dollar you risk losing on a trade, you target a profit of two or three dollars. This structure allows a trader to remain profitable overall, even if they only win 40–50% of their trades.
Realistically, no. The fundamental rule of investing is the trade-off between risk and reward. “Risk-free” assets (like U.S. Treasury bonds) typically offer the lowest returns. Any opportunity promising high returns with “no risk” is likely a scam or misrepresenting the underlying dangers.
The “sleep test” is often the best indicator. If standard market volatility causes you panic or keeps you awake at night, your portfolio is likely too aggressive for your psychological tolerance. A proper risk profile aligns your investments with your financial goals and your emotional ability to handle downturns.
Disclaimer:
Trading foreign exchange and/or contracts for difference on margin carries a high level of risk, and may not be suitable for all investors as you could sustain losses in excess of deposits. The products are intended for retail, professional and eligible counterparty clients. Before deciding to trade any products offered by PhillipCapital (DIFC) Private Limited you should carefully consider your objectives, financial situation, needs and level of experience. You should be aware of all the risks associated with trading on margin. The content of the Website must not be construed as personal advice. For retail, professional and eligible counterparty clients. Before deciding to trade any products offered by PhillipCapital (DIFC) Private Limited you should carefully consider your objectives, financial situation, needs and level of experience. You should be aware of all the risks associated with trading on margin.
Rolling Spot Contracts and CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 78% of our retail client accounts lose money while trading with us. You should consider whether you understand how Rolling Spot Contracts and CFDs work, and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
Forward-Looking Basis
Forward-Looking Basis in Futures Trading Table of Contents Introduction What...
Read MoreRebalancing Strategy
Rebalancing Strategy Mastering Portfolio Rebalancing: A Strategic Approach to Risk...
Read MoreFull Capital Protection
Full Capital Protection Understanding Full Capital Protection in Structured Products:...
Read MoreFree Cash Flow Analysis
Elevate Your Wealth Management Strategy In the sophisticated world of...
Read MoreDirect and Indirect Quotes
Direct vs. Indirect Quotes Demystifying Direct and Indirect Quotes in...
Read MoreBond Valuation Methods and Formulas
Bond Valuation Methods Mastering Bond Valuation Methods and Formulas: A...
Read MoreContrarian Investing /Dip Buying
Contrarian Investing / Dip buying Mastering the Art of Contrarian...
Read MorePartial Capital Protection
Partial Capital Protection Partial Capital Protection: The Strategic Bridge Between...
Read MoreFutures Pricing And Valuation
Futures Pricing And Valuation Table of Contents What is the...
Read MoreThe Inverse Relationship Between Bond Prices and Yields
The Inverse Relationship Between Bond Prices and Yields Table of...
Read MoreGrowth at Reasonable Price (GARP)
Growth at Reasonable Price (GARP) Mastering Growth at Reasonable Price...
Read MoreCapital Protection Structures
Capital Protection Structures Strategic Wealth Preservation: A Comprehensive Guide to...
Read Moreunderstanding dividend yield investment guide
Dividend Yield The Strategic Guide to Dividend Yield: Maximizing Passive...
Read MoreCurrent Yield vs Yield to Maturity
Understanding Current Yield vs. Yield to Maturity Understanding Current Yield...
Read MoreHow Futures Exchanges Work
How Futures Exchanges Work Understanding the Mechanics of Global Futures...
Read MoreBond Yield Vs Interest Rates
Bond Yield Vs Interest Rates Understanding the Relationship Between Bond...
Read MoreUnderstanding Exchange Rates
Understanding Exchange Rates In an increasingly interconnected global economy, the...
Read MoreBond Yield to Maturity (YTM)
Bond Yield to Maturity (YTM) Understanding Bond Yield to Maturity...
Read MoreUnderstanding Futures Contracts
Understanding Futures Contracts Understanding Futures Contracts in Global Markets In...
Read MoreCalculating Bond Price And Yield
Calculating Bond Price And Yield Understanding Bond Valuation: A Comprehensive...
Read MoreEnterprise Value And Ev/Ebitda
Enterprise Value And EV/EBITDA Enterprise Value and EV/EBITDA: A Comprehensive...
Read MorePrice-to-Sales Ratio (P/S)
Price-to-Sales Ratio (P/S) Understanding the Price-to-Sales Ratio (P/S) in Modern...
Read MorePrice-to-Book Ratio
Price-to-Book Ratio (P/B) The Essential Guide for Identifying Undervalued Stocks...
Read More




























